Understanding Insulin Resistance: What It Is and How to Prevent It.
Understanding Insulin Resistance: What It Is and How to Prevent It
Insulin resistance is a growing health concern that affects millions of people worldwide. It's a condition that can lead to serious health issues like type 2 diabetes, heart disease, and obesity. The good news is that insulin resistance is often preventable and even reversible through lifestyle changes. In this blog post, we'll explore what insulin resistance is, what causes it, and actionable steps you can take to keep your body sensitive to insulin and maintain optimal health.
What is Insulin Resistance?
Insulin is a hormone produced by the pancreas that plays a critical role in regulating blood sugar levels. It helps your body's cells absorb glucose (sugar) from the bloodstream to be used for energy or stored for later use.
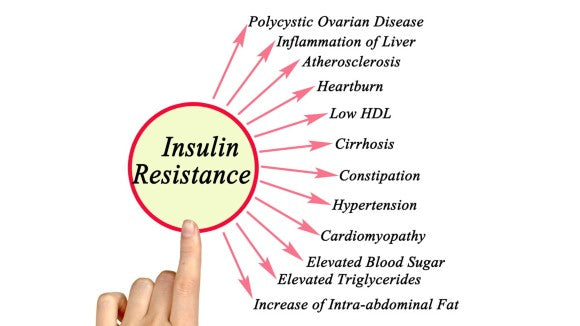
Insulin resistance occurs when the body's cells don't respond effectively to insulin. As a result, the pancreas produces more insulin to help glucose enter the cells. Over time, this can lead to elevated blood sugar levels and may progress to prediabetes or type 2 diabetes.
Key consequences of insulin resistance include:
- High blood sugar levels: Leading to various health complications.
- Increased fat storage: Particularly around the abdomen.
- Elevated insulin levels: Which can cause hormonal imbalances and inflammation.
Causes and Risk Factors of Insulin Resistance
Several factors contribute to the development of insulin resistance, including:
-
Poor Diet:
- High intake of processed foods, saturated and trans fats, and added sugars.
- Excessive consumption of refined carbohydrates like white bread and pastries.
-
Physical Inactivity:
- Sedentary lifestyle reduces the body's ability to regulate blood sugar effectively.
-
Excess Body Weight:
- Particularly fat accumulation around the abdomen increases risk.
-
Chronic Stress:
- Elevated stress hormones can interfere with insulin function.
-
Sleep Deprivation:
- Lack of quality sleep affects hormone regulation and metabolism.
-
Genetics and Family History:
- A family history of type 2 diabetes can increase susceptibility.
-
Aging:
- Insulin sensitivity tends to decrease with age.
Symptoms of Insulin Resistance
Insulin resistance can develop gradually and may not present obvious symptoms initially. However, some signs to watch out for include:
- Fatigue
- Brain fog or difficulty concentrating
- Increased hunger and cravings, especially for sweets and carbs
- Weight gain, particularly around the midsection
- High blood pressure
- Elevated blood sugar levels detected during routine check-ups
- Skin changes like dark patches (acanthosis nigricans)
If you experience these symptoms, it's essential to consult with a healthcare provider for proper assessment and guidance.
How to Prevent and Reverse Insulin Resistance
Preventing insulin resistance involves making sustainable lifestyle changes that improve your body's insulin sensitivity. Here are actionable steps you can take:
1. Adopt a Balanced and Nutrient-Rich Diet
Focus on Whole Foods:
- Fruits and Vegetables: Rich in fiber, vitamins, and antioxidants.
- Whole Grains: Such as quinoa, brown rice, and oats provide sustained energy and fiber.
- Lean Proteins: Include sources like chicken, fish, legumes, and tofu.
- Healthy Fats: Avocados, nuts, seeds, and olive oil support overall health.
Reduce Intake of:
- Processed and Sugary Foods: Limit sodas, candies, baked goods, and fast food.
- Refined Carbohydrates: Opt for whole grain alternatives over white bread and pasta.
- Saturated and Trans Fats: Found in fried foods and certain processed snacks.
Incorporate High-Fiber Foods:
- Fiber slows glucose absorption, helping regulate blood sugar levels.
- Include beans, lentils, vegetables, fruits, and whole grains in your meals.
Consider Low-Glycemic Index Foods:
- These foods cause a slower, more gradual rise in blood sugar.
- Examples include sweet potatoes, most fruits, and non-starchy vegetables.
Stay Hydrated:
- Drink plenty of water throughout the day to support metabolic processes.
2. Engage in Regular Physical Activity
Combine Different Types of Exercise:
- Aerobic Exercise: Activities like walking, jogging, cycling, or swimming improve insulin sensitivity and cardiovascular health. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic exercise per week.
- Resistance Training: Lifting weights or bodyweight exercises build muscle mass, which enhances glucose utilization. Incorporate strength training 2-3 times per week.
- High-Intensity Interval Training (HIIT): Short bursts of intense activity followed by rest periods can be particularly effective in improving insulin sensitivity.
Reduce Sedentary Behavior:
- Take short walking breaks during long periods of sitting.
- Use a standing desk or take the stairs when possible.
3. Maintain a Healthy Weight
Set Realistic Goals:
- Aim for gradual and sustainable weight loss if overweight.
- Even a 5-10% reduction in body weight can significantly improve insulin sensitivity.
Monitor Progress:
- Track your food intake, physical activity, and weight changes to stay accountable.
4. Manage Stress Effectively
Incorporate Stress-Reduction Techniques:
- Mindfulness and Meditation: Regular practice can lower stress hormones.
- Deep Breathing Exercises: Helps calm the nervous system.
- Yoga and Tai Chi: Combine physical movement with mindfulness.
- Hobbies and Leisure Activities: Engage in activities that bring joy and relaxation.
Prioritize Work-Life Balance:
- Set boundaries to ensure adequate time for rest and personal activities.
5. Ensure Quality Sleep
Establish a Consistent Sleep Schedule:
- Aim for 7-9 hours of sleep per night.
- Go to bed and wake up at the same times each day.
Create a Sleep-Conducive Environment:
- Keep your bedroom dark, quiet, and cool.
- Limit screen time before bed to improve sleep quality.
Address Sleep Disorders:
- Consult with a healthcare provider if you suspect issues like sleep apnea or insomnia.
6. Limit Alcohol and Quit Smoking
Alcohol Consumption:
- Drink in moderation, if at all. Excessive alcohol can affect blood sugar control.
Smoking Cessation:
- Smoking contributes to insulin resistance and various other health issues. Seek support to quit smoking effectively.
7. Regular Health Check-ups
Monitor Health Metrics:
- Get regular screenings for blood sugar levels, cholesterol, and blood pressure.
Consult Healthcare Professionals:
- Work with your doctor to assess risk factors and develop a personalized prevention plan.
Conclusion
Preventing insulin resistance is achievable through mindful and consistent lifestyle choices centered around healthy eating, regular physical activity, stress management, and adequate sleep. By taking proactive steps today, you can significantly reduce your risk of developing insulin resistance and its associated health complications, leading to a healthier and more vibrant life.
Remember, small, consistent changes can make a big difference over time. Start incorporating these habits into your daily routine and take control of your health journey today.



